-
 E-mail:
aceally4@aceallygroup.com
E-mail:
aceally4@aceallygroup.com
-
 Wechat: a18350222213
Wechat: a18350222213
-
Time:4/14/2025
-
Time:4/8/2025

- CONTACT US
- Wechat: a18350222213
- aceally4@aceallygroup.com
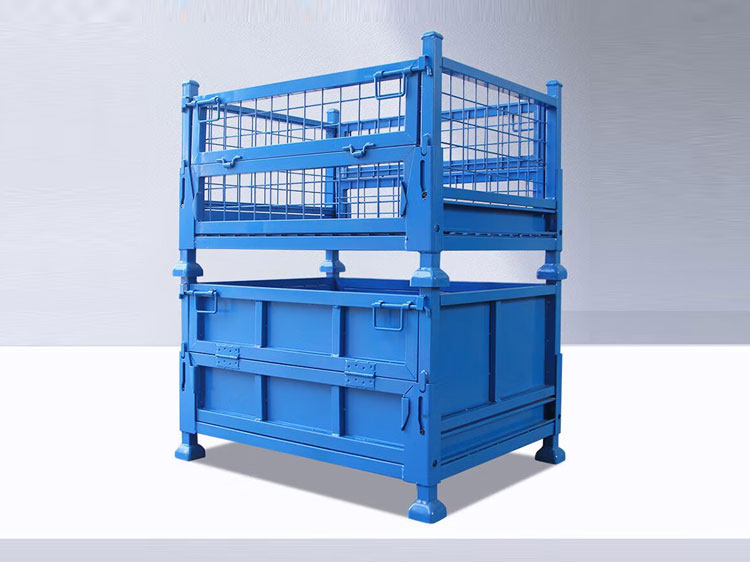
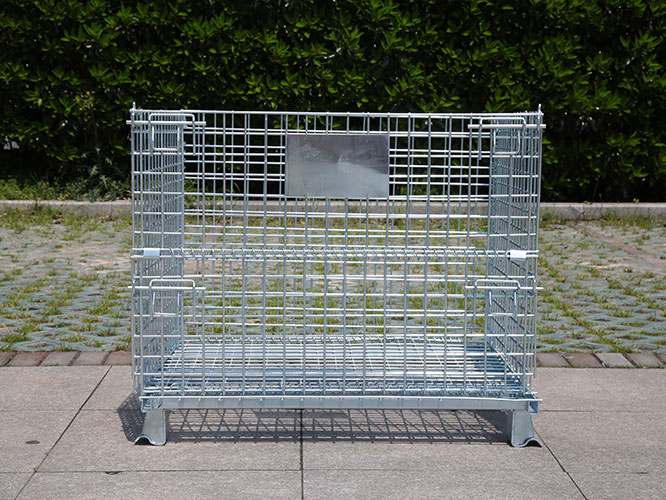
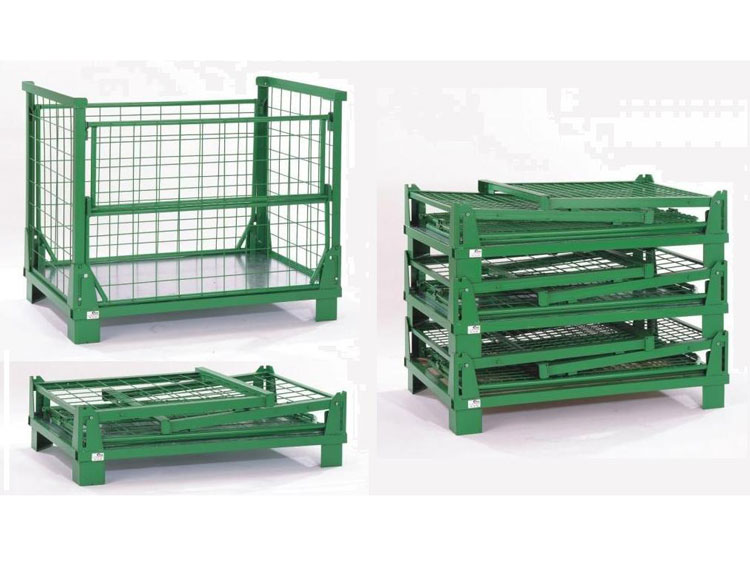
How does the design of a stillage cage ensure its strength and stability?
 Time:3/21/2025
Time:3/21/2025 111
111
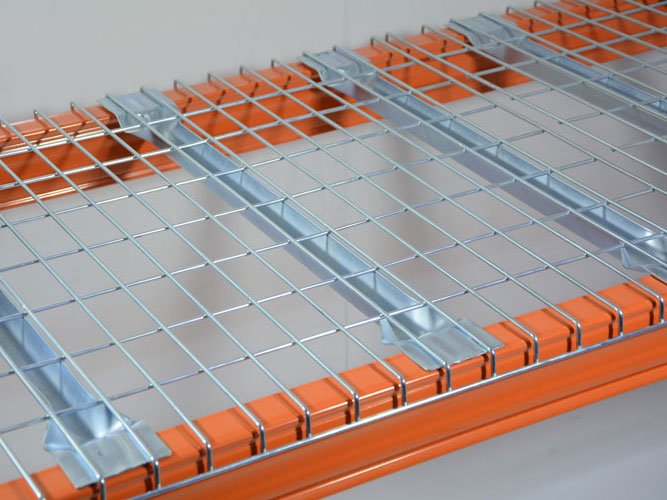
- Material Selection
High-Strength Metals: Stillage cages are usually made of high-strength steel or metal alloys. These materials have high tensile strength and yield strength, which can withstand large loads without significant deformation or breakage.
Optimal Material Thickness: The thickness of the materials used is carefully calculated and designed according to the expected load-bearing requirements. The main load-bearing components, such as the frame and support legs, adopt thicker materials to enhance their load-bearing capacity.
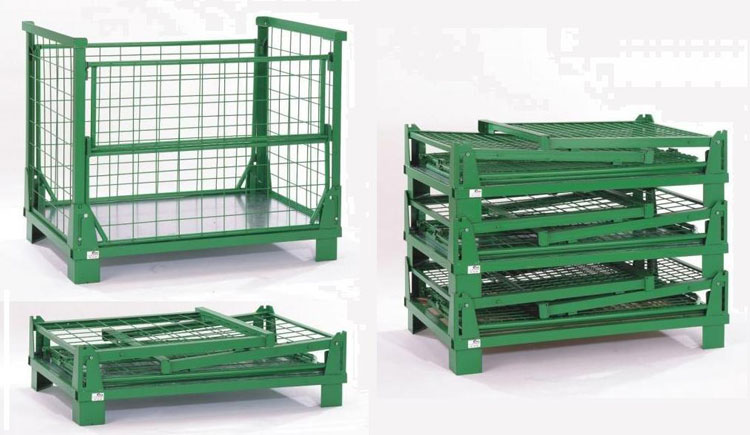

- Structural Design
Frame Structure: The frame of the stillage cage is often designed in a rectangular or square shape, which is composed of longitudinal and transverse beams to form a stable framework structure. This structure can evenly distribute the weight of the goods to each support point, reducing the stress concentration on a single component.
Triangular Reinforcement: Triangular structures are added at the joints of the frame and other key parts. The stability of the triangle is used to enhance the overall strength of the stillage cage and prevent deformation of the frame at the joints.
Bottom Support Design: The bottom of the stillage cage is designed with a reasonable support structure. The support legs are evenly distributed at the bottom of the cage to ensure that the weight of the cage and the goods are evenly transmitted to the ground, increasing stability.
- Connection Design
Welding Technology: High-quality welding technology is used to connect the components of the stillage cage to ensure a strong and reliable connection. The welding seams are carefully inspected to avoid problems such as welding porosity and lack of penetration, which can affect the strength of the connection.
Mechanical Connections: In addition to welding, some stillage cages also use mechanical connection methods such as bolts and nuts. These connections can also provide reliable fixation and are convenient for disassembly and assembly when necessary.
- Surface Treatment
Anti-Corrosion Treatment: The surface of the stillage cage is usually treated with anti-corrosion coatings, such as painting, galvanizing, etc. These treatments can prevent the metal from rusting and corroding, maintain the original mechanical properties of the material, and ensure the long-term strength and stability of the stillage cage.